Discover the Fascinating World of Common Dolphins: Characteristics, Behavior, and Conservation
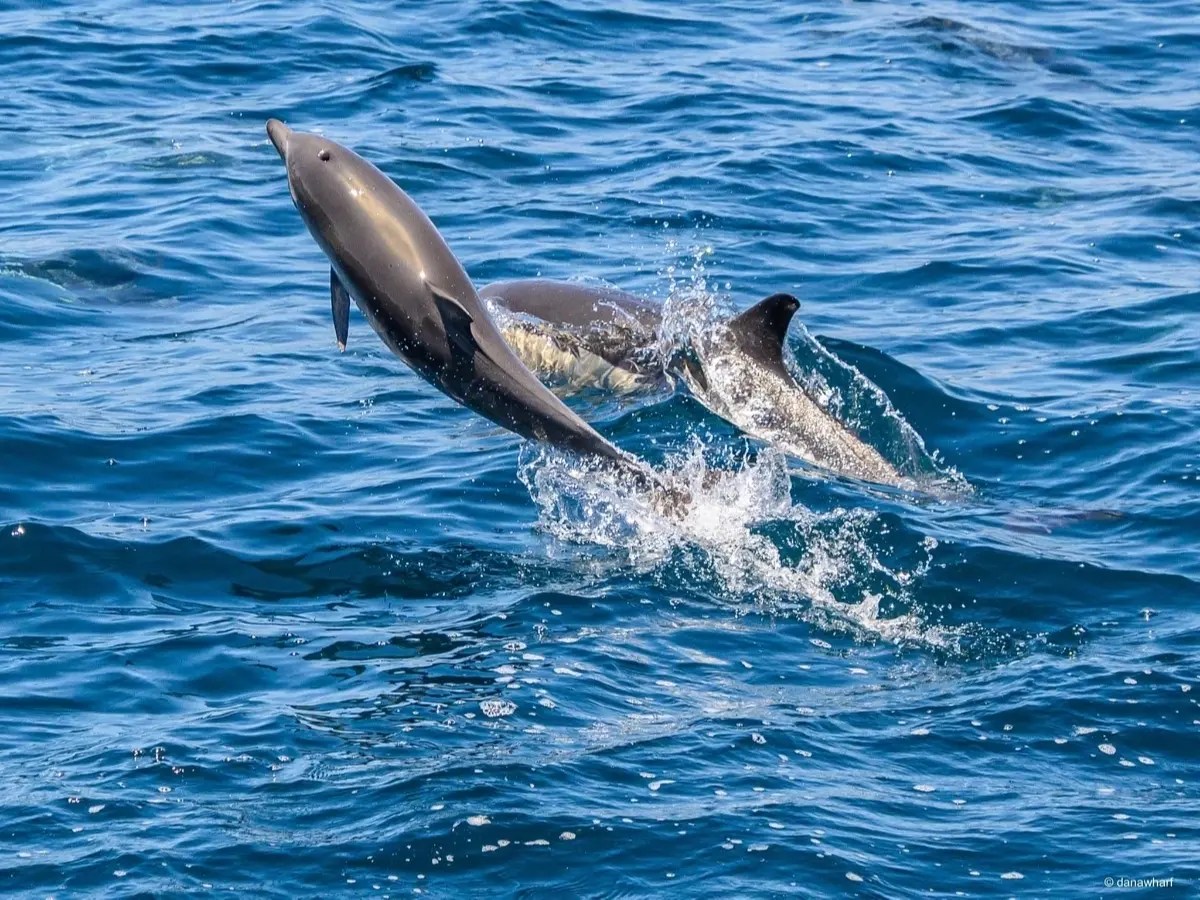

Dolphins are indeed some of the most captivating and beloved creatures in the world’s oceans, and among them, the common dolphin stands out for its widespread distribution and fascinating characteristics. Spotting a common dolphin off the coast of Dana Point, CA on one of our tours, is very likely as these creatures are highly sociable.
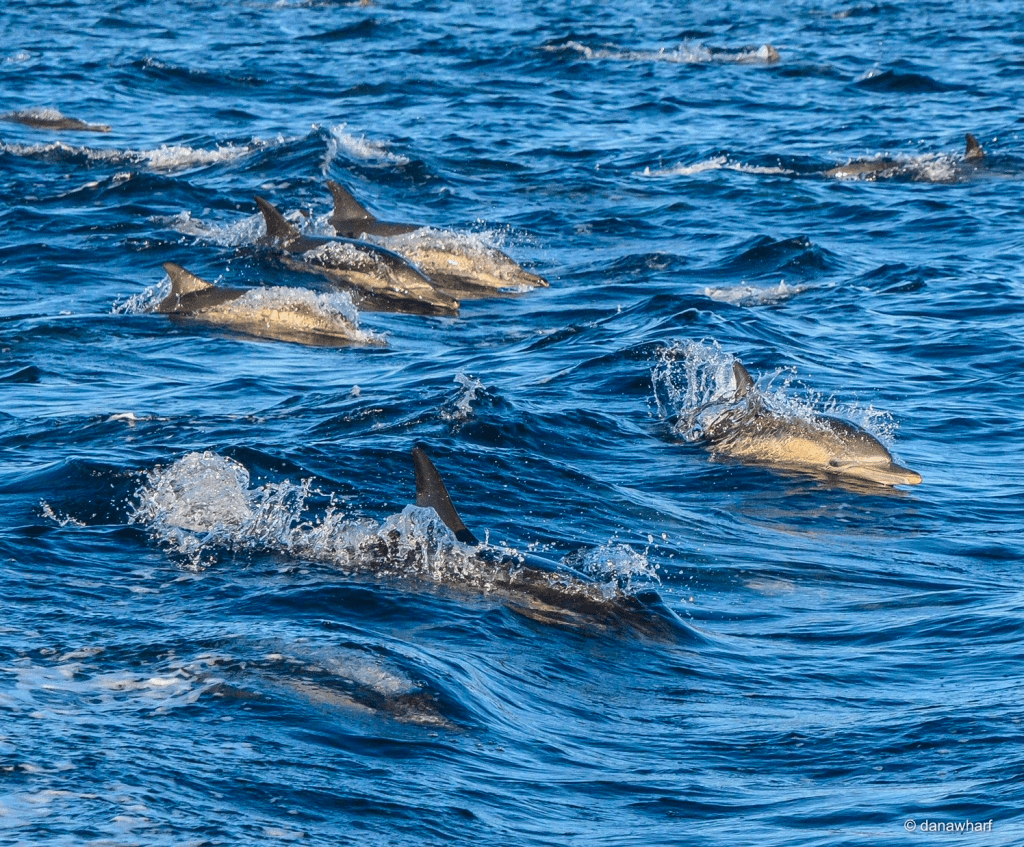

Physical Characteristics & Life Span: Common dolphins, scientifically known as Delphinus delphis, have evolved to be highly adapted to their aquatic environment. They are known for their sleek, streamlined bodies, which enable them to move through the water with incredible speed and agility.
These dolphins typically measure between 6 to 8 feet in length and weigh between 170 to 250
pounds. One of their most distinctive features is the hourglass-shaped markings on their sides, which range in color from light gray to dark brown. They also sport a long snout, a curved dorsal fin, and a powerful tail, all of which aid in their swimming abilities.
They typically live 25–35 years in the wild; lifespans in captivity are usually shorter.
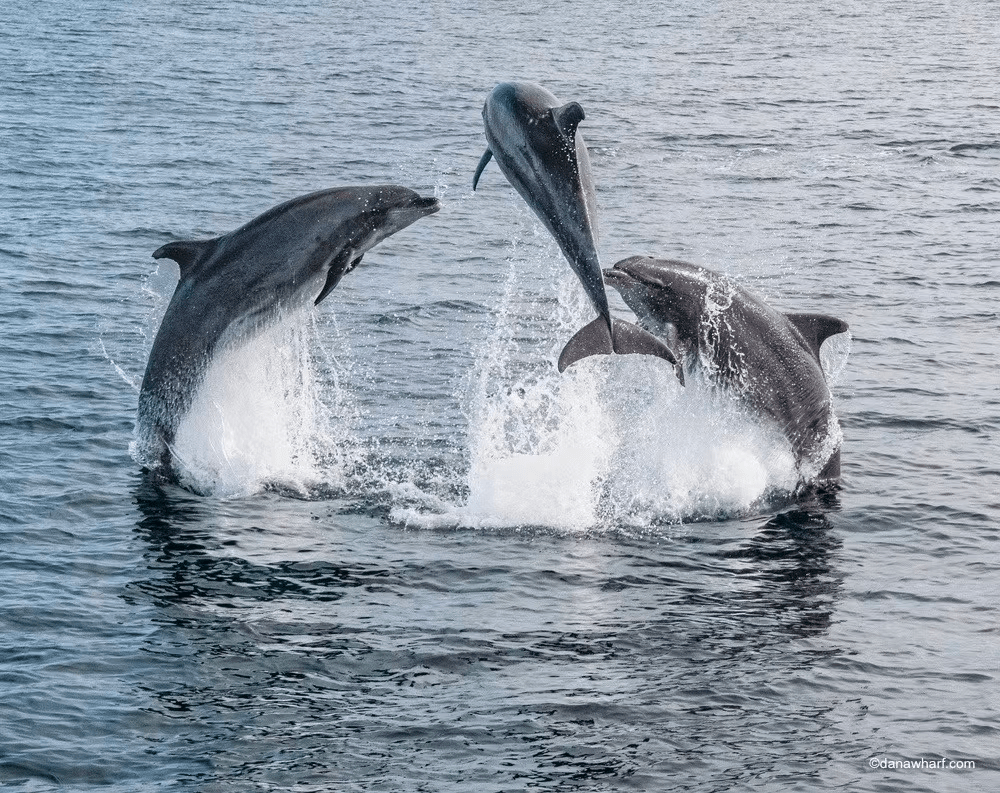
Social Behavior & Communication: Common dolphins are known for their intelligence, with studies indicating that they exhibit problem-solving skills, memory, and a capacity for learning complex tasks. Their cognitive abilities have made them subjects of scientific research to better understand the extent of their intellectual capabilities.
Common dolphins are highly sociable creatures, and they often travel in large groups known as pods. These pods can vary in size from just a few individuals to several hundred dolphins. Within these pods, they exhibit complex social interactions and communicate using a sophisticated language of clicks, whistles, and body movements. Their playful nature is evident in their frequent displays of leaping, tail-slapping, and chasing each other, earning them the reputation of being the entertainers of the sea.
These dolphins possess a sophisticated echolocation system, emitting clicks that bounce off objects in their environment and provide them with valuable information about their surroundings. This ability aids in hunting and navigation, showcasing their impressive sensory capabilities.
Beyond clicks and whistles, common dolphins engage in intricate vocalizations to convey information within their pods. These vocalizations play a crucial role in maintaining social bonds, coordinating group movements, and signaling potential threats.
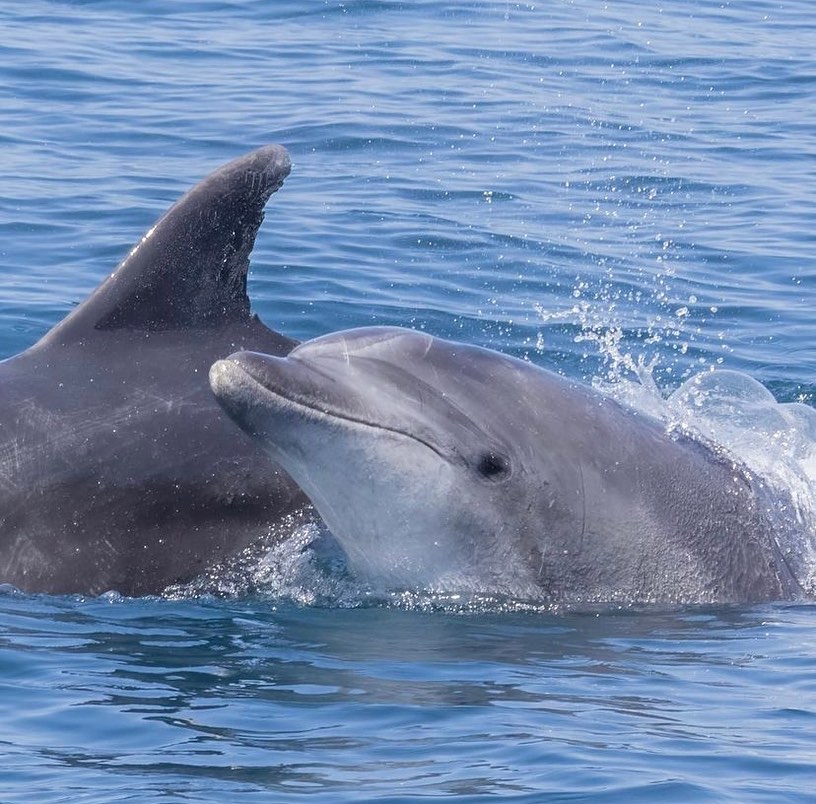

Feeding Habits: Common dolphins are opportunistic feeders with a diverse diet. They primarily prey on small fish such as herring, mackerel, and anchovies. In addition to fish, they also consume squid and crustaceans.
What’s particularly remarkable is their hunting strategy, as they often work together in coordinated groups to herd schools of fish into tight balls, making it easier for them to catch their prey. This cooperative hunting behavior highlights not only their intelligence but also their ability to collaborate as a team.
Distribution and Migration: These dolphins have a global presence, inhabiting both warm and temperate waters around the world. They exhibit seasonal migrations, following the movements of their prey. During the summer months, they can be found in cooler waters, while in the winter, they migrate to warmer waters.
Some populations even undertake extensive long-distance migrations, traveling hundreds or thousands of miles in search of food. This migratory behavior showcases their adaptability and resilience in varying marine environments.
Common dolphins typically reach sexual maturity between the ages of 5 and 10 years. Their mating season varies by region, but it often occurs during the summer months. Female dolphins have a gestation period of approximately 10 to 11 months, after which they give birth to a single calf. The mother provides care and nourishment to the calf through nursing.
Conservation Status: Despite their widespread distribution, common dolphins face several threats that have led to population declines in certain regions. Pollution, habitat degradation, and accidental capture in fishing nets are among the primary threats they encounter. Consequently, some populations of common dolphins are classified as near threatened.
Conservation efforts are actively underway to protect these magnificent creatures and their habitats. These efforts emphasize sustainable fishing practices and pollution control to ensure their survival for future generations to enjoy.
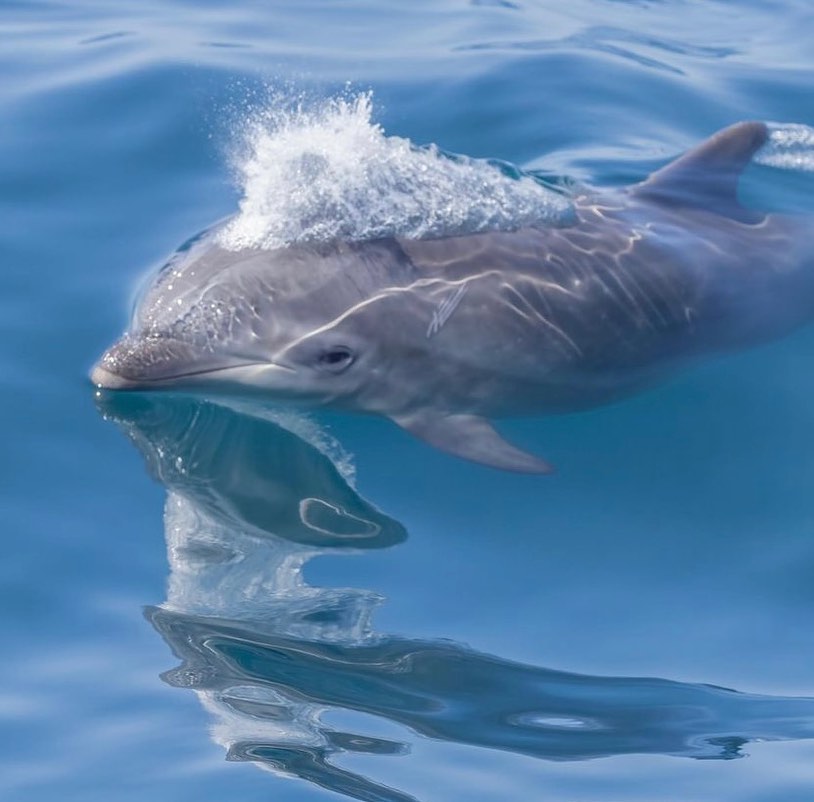

Dolphins and Human Interaction: Common dolphins have a long history of interaction with humans. They are popular attractions in marine parks and aquariums due to their acrobatic displays and ability to learn tricks. Additionally, they are the subject of numerous scientific studies because of their intelligence and complex social structures. However, not all interactions have been positive. Dolphins often fall victim to bycatch, where they are unintentionally caught in fishing nets. Concerns also exist about the impact of marine tourism on dolphin populations, emphasizing the need for responsible and ethical wildlife viewing practices.
